IBM Research macht erstmals einen Quantencomputer öffentlich zugänglich. Ab sofort kann jeder Interessierte mittels Desktop-Computer oder Mobilgerät über die IBM Cloud auf einen Quantenprozessor bestehend aus fünf Quantenbits (Qubits) zugreifen und Experimente durchführen. Der freie Zugang soll Innovationen hin zum praktischen Einsatz von Quantencomputern beschleunigen. Für IBM ist die Quantentechnologie die Zukunft der Informationsverarbeitung. Sie hat das Potenzial bestimmte, bisher selbst für Supercomputer unlösbare Problemstellungen in Wissenschaft und Industrie wie beispielsweise in der Pharmaforschung oder den Materialwissenschaften zu lösen.
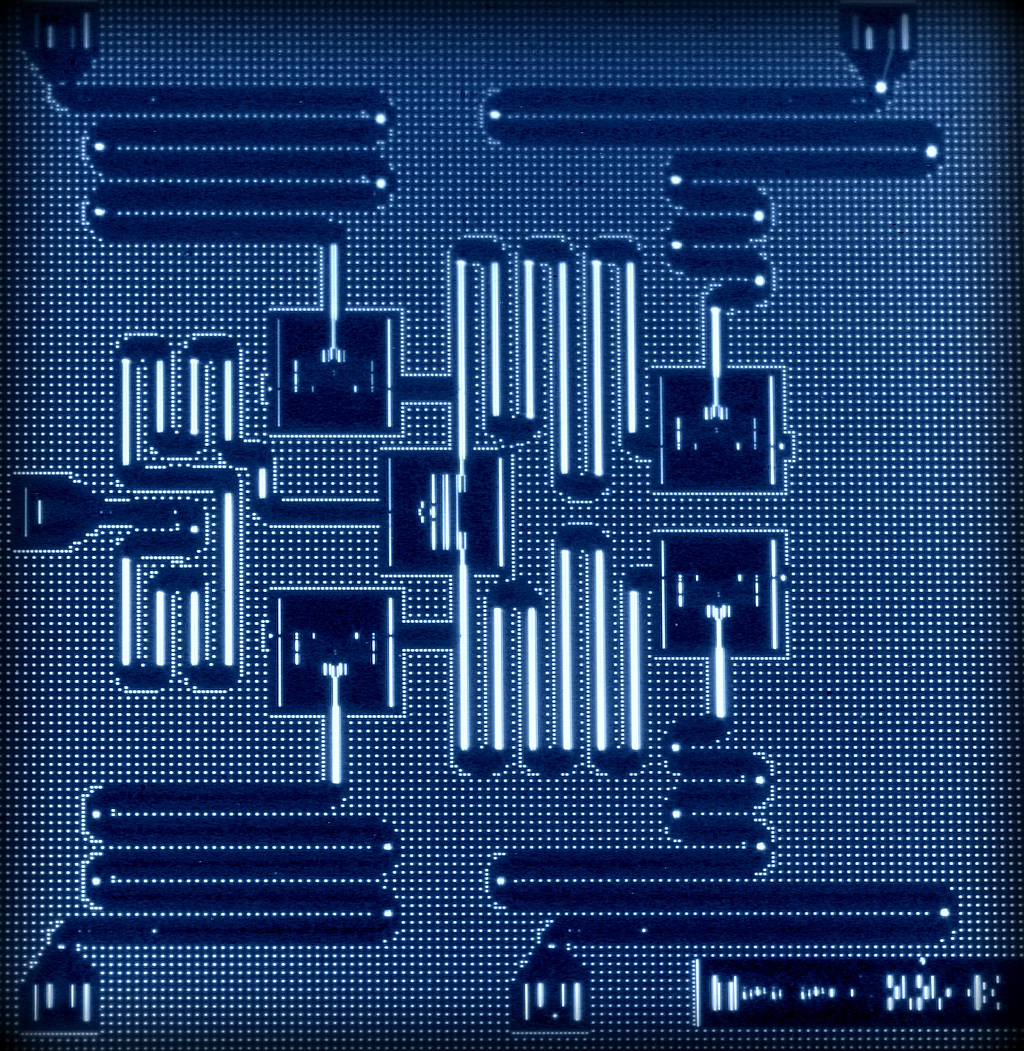
Die IBM Quantum Experience Plattform bietet Nutzern verschiedene Möglichkeiten, Quantencomputing auszuprobieren und zu entdecken: Sie können verschiedene Algorithmen testen und Experimente auf dem Quantenprozessor durchführen, mit den individuellen Qubits arbeiten sowie in Online-Seminaren und Simulationen mehr darüber erfahren, was Quantencomputer alles möglich machen könnten. Der von IBM zur Verfügung gestellte Quantenprozessor befindet sich am IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, dem Hauptsitz der IBM Forschung in Yorktown Heights, New York, U.S.A.. Er besteht aus fünf supraleitenden Qubits auf einem Siliziumchip. Die Qubits wurden mittels eines Standardverfahrens der Siliziumtechnologie hergestellt. Die hierbei verwendete Architektur von IBM Research erlaubt die Skalierung auf größere Quantensysteme und ist der führende Ansatz zum Bau eines universellen Quantencomputers.
Ein universeller Quantencomputer kann für die Berechnung jeder Aufgabe programmiert werden und für einige wichtige Anwendungen in Wissenschaft und Industrie exponentiell schneller sein als klassische Computer. Heute gibt es noch keine derartigen Computer, aber IBM erwartet, dass mittelgroße Systeme mit 50-100 Qubits im nächsten Jahrzehnt realisiert werden können. Ein Quantencomputer mit gerade einmal 50 Qubits könnte durch keinen Superrechner der gegenwärtigen TOP500-Liste emuliert werden. Dies zeigt eindrucksvoll das enorme Potenzial dieser Technologie.
Wissenschaftler arbeiten daher mit Hochdruck daran, diese Rechenleistung nutzbar zu machen. Anwendungen bei Optimierungsproblemen und der chemischen Forschung werden voraussichtlich die ersten sein, die durch Quantencomputer massiv beschleunigt werden können.
»Quantencomputer unterscheiden sich erheblich von heutigen Computern – nicht nur in ihren Bestandteilen, sondern besonders in dem, was sie können. Die Quantentechnologie wird gerade zur Realität und mit ihr werden die Möglichkeiten von computergestützten Berechnungen weit über das heute Vorstellbare hinaus erweitert«, sagt Arvind Krishna, Senior Vice President und Direktor von IBM Research. »Dies ist die Geburtsstunde des Cloud-basierten Quantencomputings. Indem wir der Öffentlichkeit Zugang zu IBMs experimentellen Quantensystem geben, wird es für Forscher und die wissenschaftliche Gemeinschaft einfacher, Innovationen im Bereich der Quantentechnologie voranzutreiben und neue Anwendungsfelder zu entdecken.«
IBM Quantum Experience
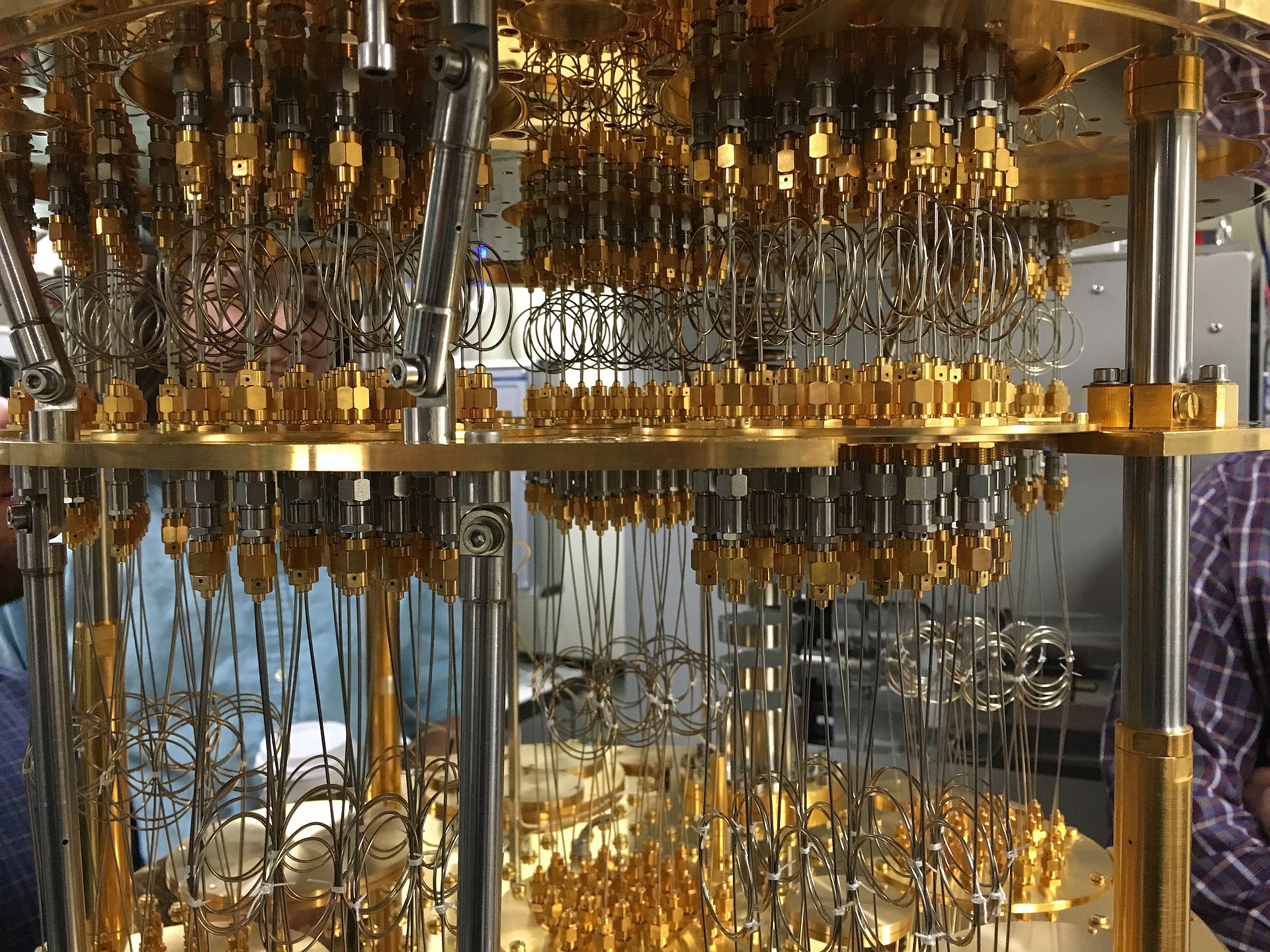
Quanteninformationen sind sehr empfindlich, da Qubits bei der Wechselwirkung mit Materie und elektromagnetischer Strahlung ihre Information verlieren. Um dies zu vermeiden, befinden sich Quantenprozessoren in einem »Tiefsttemperatur-Kühlschrank«. Den IBM-Wissenschaftlern gelangen erst im letzten Jahr einige wichtige Entwicklungsfortschritte sowohl in der Herstellung der Qubits als auch bei deren elektronischen Ansteuerung, um so den Nutzern der IBM Quantum Experience Plattform erstmals einen Prozessor mit fünf Qubits zur Verfügung zu stellen.
In Verbindung mit der Software-Expertise von IBM Research entwickelten die Forscher ein dynamisches Benutzerinterface, das es Nutzern erlaubt, einfach über die Cloud auf den Quantencomputer zuzugreifen. Für das Team ist dies nur der Beginn einer neuen Anwendergemeinschaft, die sich mit Quantencomputern und ihren Fähigkeiten befasst. Zukünftig haben die Nutzer die Möglichkeit, mit ihren Ergebnissen zu dieser Community auf der IBM Quantum Experience Plattform beizutragen. Die IBM-Wissenschaftler werden zukünftig ihre neuesten Forschungsfortschritte dort ebenfalls veröffentlichen.
IBM plant nach und nach weitere Qubits und neue Prozessor-Generationen zu IBM Quantum Experience hinzuzufügen, damit die Nutzer neue Erfahrungen sammeln und dabei helfen können, neue Anwendungen für diese Technologie zu entdecken.
Mit dem offenen Zugang zur IBM Quantum Experience können Unternehmen und Organisationen nun beginnen, das Potenzial dieser Technologie für sich zu erschließen. Außerdem bietet sich für Universitäten die Möglichkeit, ihr Unterrichtsprogramm in Quantencomputing und verwandten Bereichen anhand von konkreten Anwendungsbeispielen auszubauen. Studenten erhalten die Gelegenheit, sich mit vielversprechenden neuen Karrierewegen in Quantentechnologie vertraut zu machen.
Was ist Quantencomputing?
Die grundlegendste Information, die ein Computer versteht, ist das Bit. Vergleichbar mit einem Lichtschalter, der ein- und ausgeschaltet werden kann, hat ein Bit die zwei Zustände »1« oder »0«. Ein Quantenbit kann ebenfalls »1« oder »0«, aber auch beide Zustände gleichzeitig annehmen. Dies wird als Superposition oder beispielsweise als »0+1« bezeichnet. Das Vorzeichen dieser Superposition ist wichtig, da beide Zustände »0« und »1« eine Phasenbeziehung miteinander haben.
Diese Superpositionseigenschaft ermöglicht dem Quantencomputer, die richtige Lösung unter Millionen von Möglichkeiten viel schneller als konventionelle Computer herauszusuchen.
Da Quanteninformationen so empfindlich sind, ist die Korrektur von Quantenfehlern eine wesentliche Voraussetzung für den Bau eines universellen Quantencomputers. Letztes Jahr präsentierten IBM Wissenschaftler erstmals einen Schaltkreis aus vier, in einem quadratischen Gitter angeordneten Quantenbits. Dieser entspricht der kleinsten vollständigen Einheit eines skalierbaren Quantencomputers mit Quantenfehlerkorrektur. Denn mit dieser Anordnung können die zwei Arten von Quantenfehlern (sogenannte Bit-flip- und Phase-flip-Fehler), die in jedem Quantencomputer auftreten können, entdeckt und gemessen werden.
Nun gelang den Wissenschaftlern durch die Kombination von fünf Qubits in der Gitterstruktur ein weiterer wichtiger Schritt hin zum Universalquantencomputer. Die Anordnung mit insgesamt fünf Qubits erlaubt eine Messung der Parität (binäre Quersumme) von vier benachbarten Qubits. Dies ist eine der wichtigsten logischen Operationen in Quantencomputern und die Basis von vielen Protokollen zur Quantenfehlerkorrektur.
IBM Research Frontiers Institut
Die Quantencomputer-Plattform IBM Quantum Experience ist eine Kerninitiative des neu gegründeten IBM Research Frontiers Institut. Das Frontiers Institut ist ein Konsortium zur Entwicklung von bahnbrechenden IT- und Computertechnologien, um wegweisende Innovationen voranzutreiben. Unternehmen von verschiedensten Industrien können IBMs Forschungsexpertise und neuste Infrastruktur nutzen, um auszuloten, welchen Einfluss Quantencomputer auf ihre Organisation und ihr Geschäftsfeld haben werden. Gründungsmitglieder des Frontiers Institute sind Samsung, JSR und Honda.
IBM Quantum Experience: www.ibm.com/quantumcomputing
Youtube-Video: Cloud-basierten Quantencomputing https://youtu.be/DZ2DcILZAbM
Youtube-Video: 360° Video des IBM Quantenlabors: https://youtu.be/jf7D8snlsnQ
Youtube-Video: Rundgang durch das IBM Quantenlabor: https://youtu.be/KZf4BSmgdO4
IBM Makes Quantum Computing Available on IBM Cloud to Accelerate Innovation
Users can run experiments on an IBM quantum processor
Yorktown Heights, N.Y., (04 May 2016) – IBM (NYSE: IBM) Research announced today that for the first time ever it is making quantum computing available to members of the public, who can access and run experiments on IBM’s quantum processor. IBM scientists have built a quantum processor that users can access through a first-of-a-kind quantum computing platform delivered via the IBM Cloud onto any desktop or mobile device. IBM believes quantum computing is the future of computing and has the potenzial to solve certain problems that are impossible to solve on today’s supercomputers. The cloud-enabled quantum computing platform, called IBM Quantum Experience, will allow users to run algorithms and experiments on IBM’s quantum processor, work with the individual quantum bits (qubits), and explore tutorials and simulations around what might be possible with quantum computing. The quantum processor is composed of five superconducting qubits and is housed at the IBM T.J. Watson Research Center in New York. The five-qubit processor represents the latest advancement in IBM’s quantum architecture that can scale to larger quantum systems. It is the leading approach towards building a universal quantum computer. A universal quantum computer can be programmed to perform any computing task and will be exponentially faster than classical computers for a number of important applications for science and business. A universal quantum computer does not exist today, but IBM envisions medium-sized quantum processors of 50-100 qubits to be possible in the next decade. With a quantum computer built of just 50 qubits, none of today’s TOP500 supercomputers could successfully emulate it, reflecting the tremendous potenzial of this technology. The community of quantum computer scientists and theorists is working to harness this power, and applications in optimization and chemistry will likely be the first to demonstrate quantum speed-up.
»Quantum computers are very different from today’s computers, not only in what they look like and are made of, but more importantly in what they can do. Quantum computing is becoming a reality and it will extend computation far beyond what is imaginable with today’s computers,” said Arvind Krishna, senior vice president and director, IBM Research. »This moment represents the birth of quantum cloud computing. By giving hands-on access to IBM’s experimental quantum systems, the IBM Quantum Experience will make it easier for researchers and the scientific community to accelerate innovations in the quantum field, and help discover new applications for this technology.”
With Moore’s Law running out of steam, quantum computing will be among the technologies that could usher in a new era of innovation across industries. This leap forward in computing could lead to the discovery of new pharmaceutical drugs and completely safeguard cloud computing systems. It could also unlock new facets of artificial intelligence (which could lead to future, more powerful Watson technologies), develop new materials science to transform industries, and search large volumes of big data.
IBM Quantum Experience
Quantum information is very fragile and needs to be protected from any errors that can result from heat and electromagnetic radiation. Signals are sent in and out of a cryogenic dilution refrigerator to measure operations on the quantum processor.
The IBM team has made a number of robust engineering advances both at the device level and in the electronic controls to give IBM Quantum Experience users unprecedented and reliably high-quality performance in this five-qubit processor. Coupled with software expertise from the IBM Research ecosystem, the team has built a dynamic user interface on the IBM Cloud platform that allows users to easily connect to the quantum hardware via the cloud. The team sees the introduction to the public of this complete quantum computing framework as just the start of a new user community, which embraces the quantum world and how it works.
In the future, users will have the opportunity to contribute and review their results in the community hosted on the IBM Quantum Experience and IBM scientists will be directly engaged to offer more research and insights on new advances. IBM plans to add more qubits and different processor arrangements to the IBM Quantum Experience over time, so users can expand their experiments and help uncover new applications for the technology.
Quantum computing – a different way of thinking
We live in a world where classical physics defines our experiences and our intuition, and ultimately how we process information. However, nature at the atomic level is governed by a different set of rules known as quantum mechanics. It is beyond the reach of classical computers to solve problems that exist in nature in which quantum mechanics plays a role, for example, understanding how molecules behave.To overcome this, in 1981, Richard Feynman proposed to build computers based on the laws of quantum mechanics. Over three decades later, IBM is helping to make this a reality.
Quantum computing works fundamentally differently from today’s computers. A classical computer makes use of bits to process information, where each bit represents either a one or a zero. In contrast, a qubit can represent a one, a zero, or both at once, which is known as superposition. This property along with other quantum effects enable quantum computers to perform certain calculations vastly faster than is possible with classical computers.
Most of today’s quantum computing research in academia and industry is focused on building a universal quantum computer. The major challenges include creating qubits of high quality and packaging them together in a scalable way, so they can perform complex calculations in a controllable way.
IBM employs superconducting qubits that are made with superconducting metals on a silicon chip and can be designed and manufactured using standard silicon fabrication techniques. Last year, IBM scientists demonstrated critical breakthroughs to detect quantum errors by combining superconducting qubits in latticed arrangements, and whose quantum circuit design is the only physical architecture that can scale to larger dimensions.
Now, IBM scientists have achieved a further advance by combining five qubits in the lattice architecture, which demonstrates a key operation known as a parity measurement – the basis of many quantum error correction protocols. The road towards universal quantum computing hinges upon the achievement of quantum error correction, and the IBM team has taken another important step down this challenging path.
New frontiers for quantum computing
There has been tremendous progress and interest in the field of quantum of computing in recent years. By giving users access to the IBM Quantum Experience, it will help businesses and organizations begin to understand the technology’s potenzial, for universities to grow their teaching programs in quantum computing and related subjects, and for students to become aware of promising new career paths.
»It is a beautiful challenge to pursue the path to build the first universal quantum computer, but it requires us to change how we think about the world. Access to early quantum computing prototypes will be key in imagining and developing future applications,” said Dario Gil, vice president of science & solutions, IBM Research. »If you want to understand what a true quantum computer will do for you and how it works, this is the place to do it. You won’t experience it anywhere else.”
IBM’s quantum computing platform is a core initiative within the newly formed IBM Research Frontiers Institute. The Frontiers Institute is a consortium that develops and shares ground-breaking computing technologies to spur world-changing innovations. Companies from diverse industries can leverage IBM’s research talent and cutting-edge infrastructure to explore what the future of quantum computing may mean for their organization and business.
To access the IBM Quantum Experience and for more information on IBM’s quantum computing research, please visit www.ibm.com/quantumcomputing.
About IBM Research
For more than seven decades, IBM Research has defined the future of information technology with more than 3,000 researchers in 12 labs located across six continents. Scientists from IBM Research have produced six Nobel Laureates, 10 U.S. National Medals of Technology, five U.S. National Medals of Science, six Turing Awards, 19 inductees in the National Academy of Sciences and 20 inductees into the U.S. National Inventors Hall of Fame. For more information about IBM Research, visit www.ibm.com/research.