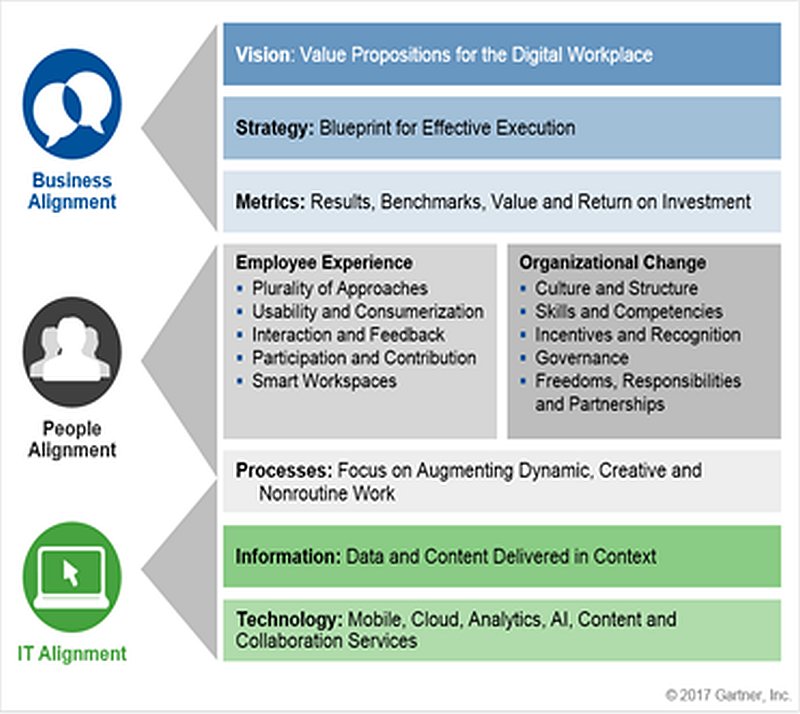
Von der elektronischen Signatur bis zur sicheren, digitalen Dokumentenablage – der technologische Fortschritt hat viele administrative Aufgaben vereinfacht. Die Digital-Workplace-Studie, welche in Zusammenarbeit mit Adobe entstanden ist, beleuchtet den Büroalltag der Wissensarbeiter in Deutschland und die Chancen der Digitalisierung von administrativen Prozessen. Sonja Köhn
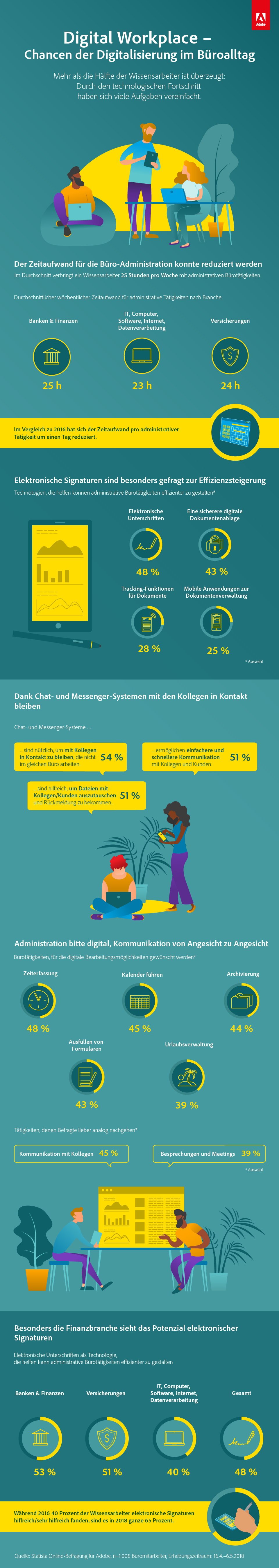
Digitalisierung: Kann digitale Technologie die Welt besser machen?
38 Prozent der deutschen Teilnehmer des Digital Society Index 2018 [1] glauben, dass die Digitalisierung zur Lösung der dringendsten Herausforderungen (z.B. Armut, Gesundheitsprobleme, Umweltzerstörung) der Welt beitragen wird. Damit ist der technologische Zukunftsoptimismus der Bundesbürger im Vergleich eher wenig ausgeprägt, wie der Blick auf die Grafik zeigt. Anders sieht das in China aus: 71 Prozent der Befragten dort sind der Meinung, dass digitale Technologie die Welt besser machen kann. Mathias Bran
[1] https://dan.hu/en/digital-society-index-2018-2/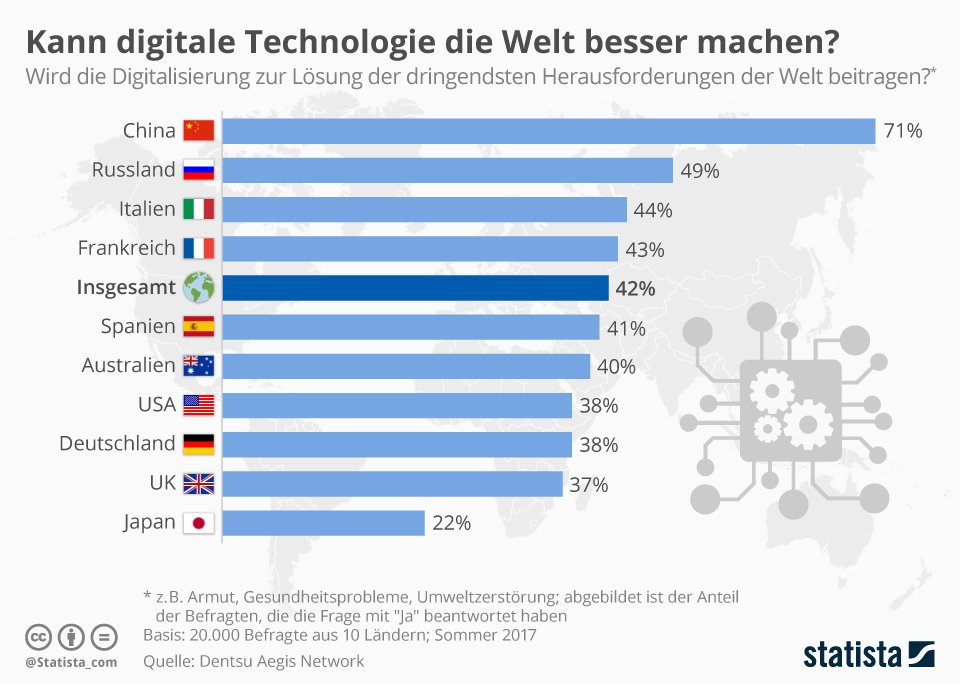
https://de.statista.com/infografik/15854/beitrag-der-digitalisierung-zur-loesung-der-dringendsten-herausforderungen-der-welt/
Acht erfolgsentscheidende Bestandteile eines Digital Workplace
Programme zur Schaffung von Digital Workplaces geraten häufig auf Abwege oder scheitern zur Gänze. Dem IT-Research und Beratungsunternehmen Gartner zufolge liegt das meistens an einer fragmentierten Herangehensweise, bei der isolierte technische Lösungen wichtiger genommen werden als die Gesamtstrategie. Wer in Unternehmen für das Thema Digital Workplace verantwortlich ist, muss sicherstellen, dass die Digital-Workplace-Initiativen alle acht entscheidenden Komponenten für eine erfolgreiche Implementierung enthalten.
»Der Digital Workplace verspricht eine flexiblere, interaktivere und intelligentere Arbeitsumgebung zur Nutzung des sich ändernden geschäftlichen Umfeldes«, erklärt Carol Rozwell, Vice President und Distinguished Analyst bei Gartner. »Für ihren Erfolg muss klar sein, dass Digital Workplaces nicht im Vakuum existieren. Sie müssen Teil einer umfassenden Unternehmensstrategie sein, die das Ziel verfolgt, die Agilität und das Engagement der Mitarbeiter durch eine ‚konsumerisierte‘ Arbeitsumgebung zu erhöhen, die den privaten Verbraucher im Mitarbeiter anspricht.«
Gartner Highlights Eight Critical Components of a Digital Workplace
Analysts to Discuss Latest Digital Workplace Best Practices at Gartner Digital Workplace Summit, 18-19 September 2017 in London, UK
Digital workplace programs often lose their way, or fail, due to a fragmented approach that prioritises a few technology »fixes« over business strategy, said Gartner, Inc. To combat this, digital workplace leaders need to employ a framework to ensure their digital workplace initiatives address all of the eight critical components required for a successful implementation.
»The digital workplace promises a more flexible, engaging and intelligent work environment that is able to exploit changing business conditions,« said Carol Rozwell, vice president and distinguished analyst at Gartner. »To be successful, a digital workplace can’t be built in a vacuum. It must be part of a wider business strategy that seeks to boost employee agility and engagement by developing a more consumerised work environment.«
Gartner has identified the eight critical components — »building blocks« — that application leaders need when planning, directing and evolving digital workplace programmes (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. The Eight Building Blocks of a Digital Workplace
Source: Gartner (August 2017)
- Vision: Describe What Digital Workplace Success Will Look Like
The vision describes the future state of the digital workplace and how it will benefit all stakeholders. It should be consistent with the organisation’s values and serve as a source of inspiration to the stakeholders who will craft the strategy and tactics to realise the vision. - Strategy: Create a Roadmap to Reach the Destination
The strategy describes the approach an organisation will use to achieve its vision and create a digitally empowered workforce. It clearly defines the strategic roadmap to achieve the organisation’s business goals. - Metrics: Measure Performance and Value
How application leaders of digital workplace programmes measure the value of their initiatives should be an extension of the organisation’s current approach. Each initiative should be designed to have a positive impact on a business value metric, such as workforce effectiveness, employee agility, employee satisfaction and employee retention. Effective metrics also provide a feedback mechanism for continuous development of strategy and tactics, serve as great tools for change management, and help structure employee incentives. - Employee Experience: Design for Improved Employee Interaction
Creating an excellent employee experience is a pivotal aspect of a digital workplace. An engaged, creative and energetic workforce outperforms the competition in terms of service delivery, execution and product design. »The aim should be to increase employees‘ participation in any workplace redesign, in order to create an environment that will make them more effective and connect them better to the outcomes of the business,« said Ms Rozwell. - Organisational Change: Start Small but Think Big
As digital workplace initiatives mature, they require considerable change to an organisation’s internal processes, departmental structures, incentives, skills, culture and behaviour. Ultimately, digital workplace initiatives will affect every system, process and role within the organisation. - Processes: Re-engineer How High-Impact Work Is Done
Digital workplace programmes are particularly powerful when they set their sights on increasing the effectiveness of people who do high-impact work. Such work benefits from more agile, responsive and collaborative processes that rely more on the ability to respond rapidly to changing circumstances. Re-engineering business processes requires a close look at how employees currently work, in order to design new work journeys. The new and improved ways of working will involve the addition of new tools to enable collaborative work, use of other new technologies and adaptation of outmoded processes. - Information: Rework Access and Use of Content and Analytics
Workers expect enterprise tools for searching, sharing and consuming information to be as »smart« and compelling as those they use in their personal lives. They want information and analytics to be contextualised, based on their work, and delivered when they need it. By 2020, algorithms will improve the behaviour of over 1 billion workers. - Technology: Take a Platform Approach to Workplace Investments
Application leaders responsible for digital workplace programmes must work out how to use technology to reach customers, internet-connected »things« and ecosystems. They must also determine how new technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can enable more effective ways of working, and how to exploit the next wave of technology innovation without having to constantly rearchitect.
[1] More detailed analysis is available to Gartner clients in the report »Eight Building Blocks You Need to Construct Your Digital Workplace Plan.«
Gartner Digital Workplace Summit
Digital workplace trends will be further discussed at the Gartner Digital Workplace Summit 2017, taking place 18-19 September in London, UK. Follow news and updates from the event on Twitter at#GartnerDWS.
Hier folgt eine Auswahl an Fachbeiträgen, Studien, Stories und Statistiken die zu diesem Thema passen. Geben Sie in der »Artikelsuche…« rechts oben Ihre Suchbegriffe ein um weitere Artikel zu finden.